Building a Newsletter App with Upstash Workflow and Redis
In this blog, we will build a newsletter app where users will be able to subscribe and select how often they want to recieve their newsletters. We will use Upstash Redis to store the subscription data and Upstash Workflow to manage the actions of storing data, sending welcome emails, and scheduling newsletters based on the user's preferences.
Motivation
First of all, serverless environments are great! They are highly scalable and easy on the budget. However, they come with certain limitations, such as execution time limits. This can especially be problematic when you need to run long-running tasks.
That's where Upstash Workflow comes into play. With Upstash Workflow, you can create persistent workflows that can run as long as they need to. So, you don't have to worry about serverless function timeouts anymore.
Here is a list of features that you get when using Upstash Workflow:
- No more serverless function timeouts: Your workflows can run as long as they need to.
- Automatic recovery: If something goes wrong and a workflow fails midway, it automatically recovers.
- Automatic retries: If any step in the workflow fails, it will be retried automatically.
- Real-time monitoring: You can monitor your workflows in real-time from the Upstash Console.
Prerequisites
- Basic understanding of Next.js applications.
- An Upstash account for Redis and QStash tokens.
- Vercel account for deployment.
- ngrok (recommended) for local development.
Project Setup
Let's start by bootstrapping a new Next.js project using create-next-app:
npx create-next-app@latest --typescript newsletter-app
cd newsletter-appNow, let's add the necessary dependencies to interact with Upstash QStash and Redis services:
npm install @upstash/qstash @upstash/redisDirectory Structure
Before diving into the code, let's take a quick look at how we'll organize our project:
src/app/: This is where our main application components and pages will live.src/app/api/: We'll put our API routes here—for subscribing, unsubscribing, and handling workflows.src/components/: This folder will contain our subscription and unsubscription form components.src/lib/: Utility functions for Redis and email sending will go here.src/types/: We'll keep our TypeScript type definitions in this directory.
Environment Variables
We need to create a .env file at the root of our project and add the following:
QSTASH_TOKEN=
UPSTASH_REDIS_REST_URL=
UPSTASH_REDIS_REST_TOKEN=
EMAIL_SERVICE_URL=
NEXT_PUBLIC_BASE_URL=- QSTASH_TOKEN: Our Upstash QStash token accessed from the Upstash Console.
- UPSTASH_REDIS_REST_URL and UPSTASH_REDIS_REST_TOKEN: Our Upstash Redis credentials accessed from the Upstash Console.
- EMAIL_SERVICE_URL: The endpoint of our email sending API.
- NEXT_PUBLIC_BASE_URL: The base URL of our deployed application (e.g.,
https://your-app.vercel.app).
We can also set the UPSTASH_WORKFLOW_URL variable in our .env file for local development with our ngrok URL. To learn more about how to develop workflows locally with ngrok, refer to the Upstash Documentation.
The UPSTASH_WORKFLOW_URL environment variable is only necessary for local development. In production, the baseUrl parameter is automatically set and can be omitted.
Project Implementation
Subscription Form Component
The SubscriptionForm component allows users to enter their email and select how often they want to receive the newsletter. When the form is submitted, we send a POST request to /api/subscribe with the form data.
"use client";
import React, { useState } from "react";
export default function SubscriptionForm() {
const [frequency, setFrequency] = useState("daily");
const [showCustomFrequency, setShowCustomFrequency] = useState(false);
const [message, setMessage] = useState("");
const [isError, setIsError] = useState(false);
// Handle frequency selection
const handleFrequencyChange = (e: React.ChangeEvent<HTMLSelectElement>) => {
const value = e.target.value;
setFrequency(value);
setShowCustomFrequency(value === "custom");
};
// Handle form submission
const handleSubmit = async (e: React.FormEvent<HTMLFormElement>) => {
e.preventDefault();
setMessage("");
setIsError(false);
const formData = new FormData(e.currentTarget);
try {
const response = await fetch("/api/subscribe", {
method: "POST",
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
},
body: JSON.stringify(Object.fromEntries(formData.entries())),
});
const result = await response.json();
if (!response.ok) {
setIsError(true);
setMessage(result.error || "An error occurred during subscription.");
} else {
setIsError(false);
setMessage(result.message || "Subscription successful!");
}
} catch (error) {
console.error("An unexpected error occurred:", error);
setIsError(true);
setMessage("An unexpected error occurred.");
}
};
// Render the form
return (
<form className="flex flex-col gap-4 text-gray-700" onSubmit={handleSubmit}>
<input
type="email"
name="email"
placeholder="Your Email"
required
className="border p-2 rounded"
/>
<select
name="frequency"
value={frequency}
onChange={handleFrequencyChange}
required
className="border p-2 rounded text-gray-700"
>
<option value="daily">Daily</option>
<option value="weekly">Weekly</option>
<option value="monthly">Monthly</option>
<option value="custom">Custom Amount of Days</option>
</select>
{showCustomFrequency && (
<input
type="number"
name="customFrequency"
placeholder="Enter number of days"
min="1"
className="border p-2 rounded text-gray-700"
required
/>
)}
<button type="submit" className="bg-blue-500 text-white p-2 rounded">
Subscribe
</button>
{message && (
<p className={`mt-2 ${isError ? "text-red-500" : "text-green-500"}`}>
{message}
</p>
)}
</form>
);
}Unsubscribe Form Component
The UnsubscribeForm component allows users to enter their email to unsubscribe from the newsletter. When the form is submitted, we send a POST request to /api/unsubscribe with the email data. It also pre-fills the email field if the user clicked an unsubscribe link in one of the emails.
"use client";
import { useState, useEffect, Suspense } from "react";
import { useSearchParams } from "next/navigation";
const UnsubscribeForm = () => {
const searchParams = useSearchParams();
const [email, setEmail] = useState("");
const [message, setMessage] = useState("");
const [isError, setIsError] = useState(false);
// Pre-fill email from query parameter
useEffect(() => {
const emailParam = searchParams.get("email");
if (emailParam) {
setEmail(emailParam);
}
}, [searchParams]);
// Handle form submission
const handleSubmit = async (e: React.FormEvent) => {
e.preventDefault();
setMessage("");
setIsError(false);
try {
const response = await fetch("/api/unsubscribe", {
method: "POST",
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
},
body: JSON.stringify({ email }),
});
const data = await response.json();
if (response.ok) {
setIsError(false);
setMessage("You have been unsubscribed successfully.");
} else {
setIsError(true);
setMessage(data.error || "Something went wrong. Please try again.");
}
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error unsubscribing:", error);
setIsError(true);
setMessage("An unexpected error occurred. Please try again.");
}
};
// Render the form
return (
<form className="flex flex-col gap-4 text-gray-700" onSubmit={handleSubmit}>
<input
type="email"
name="email"
value={email}
onChange={(e) => setEmail(e.target.value)}
placeholder="Your Email"
required
className="border p-2 rounded"
/>
<button
type="submit"
className="bg-red-500 hover:bg-red-700 text-white p-2 rounded"
>
Unsubscribe
</button>
{message && (
<p className={`mt-2 ${isError ? "text-red-500" : "text-green-500"}`}>
{message}
</p>
)}
</form>
);
};
export default function UnsubscribePage() {
return (
<Suspense fallback={<div>Loading...</div>}>
<UnsubscribeForm />
</Suspense>
);
}Store Data in Redis
We'll use Upstash Redis to store user subscription data.
In order to use Upsatsh Redis, we first need to set up a Redis database on Upstash Console and get our REST URL and token. For more information on this, you can check out the Upstash Documentation.
redis.ts will contain our Redis client and helper functions for interacting with Redis:
import { Redis } from "@upstash/redis";
export const redis = new Redis({
url: process.env.UPSTASH_REDIS_REST_URL!,
token: process.env.UPSTASH_REDIS_REST_TOKEN!,
});
export async function getUserFrequency(email: string): Promise<number | null> {
const data = await redis.get(`user:${email}`);
console.log("User data:", data);
if (!data) return null;
const parsed = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(data));
return parsed.frequency;
}
export async function removeUser(email: string): Promise<void> {
await redis.del(`user:${email}`);
}
export async function checkSubscription(email: string): Promise<boolean> {
return (await getUserFrequency(email)) !== null;
}Email Sending Function
To send emails, we'll use our own email API that we developed in a previous blog post about creating an Email Scheduler with QStash Python SDK.
export async function sendEmail(message: string, email: string) {
console.log(`Sending email to ${email}`);
const url = process.env.EMAIL_SERVICE_URL;
const payload = {
to_email: email,
subject: "Upstash Newsletter",
content: message,
};
if (!url) {
console.error("EMAIL_SERVICE_URL is not defined.");
return;
}
const response = await fetch(url, {
method: "POST",
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
},
body: JSON.stringify(payload),
});
if (!response.ok) {
console.error("Failed to send email:", await response.text());
}
}Type Definitions
We also need a type definition for the subscription data:
export type SubscriptionData = {
email: string;
frequency: string;
customFrequency?: string;
};Subscribe API Route
We'll create an API route that handles subscription requests. When a user submits the subscription form, this endpoint will check if the user is already subscribed and enqueue a workflow to handle sending emails based on the user's chosen frequency.
import { NextRequest, NextResponse } from "next/server";
import { checkSubscription } from "@/lib/redis";
export const POST = async (request: NextRequest) => {
try {
const { email, frequency: freq, customFrequency } = await request.json();
console.log("Email:", email);
console.log("Frequency:", freq);
console.log("Custom Frequency:", customFrequency);
if (!email || !freq) {
console.error("Email and frequency are required.");
return NextResponse.json(
{ error: "Email and frequency are required." },
{ status: 400 }
);
}
let frequency = freq;
if (frequency === "custom") {
if (!customFrequency) {
console.error("Custom frequency days are required.");
return NextResponse.json(
{ error: "Custom frequency days are required." },
{ status: 400 }
);
}
frequency = customFrequency;
}
if (frequency === "daily") {
frequency = "1";
} else if (frequency === "weekly") {
frequency = "7";
} else if (frequency === "monthly") {
frequency = "30";
}
const frequencyNumber = Number(frequency);
if (isNaN(frequencyNumber) || frequencyNumber <= 0) {
console.error("Invalid frequency value.");
return NextResponse.json(
{ error: "Invalid frequency value." },
{ status: 400 }
);
}
const exists = await checkSubscription(email);
if (exists) {
console.error("Email is already subscribed.");
return NextResponse.json(
{ error: "Email is already subscribed." },
{ status: 400 }
);
}
console.log("Subscription successful!");
console.log("Enqueue the workflow");
// Enqueue the workflow
await fetch(`${process.env.NEXT_PUBLIC_BASE_URL}/api/workflow`, {
method: "POST",
headers: {
Authorization: `Bearer ${process.env.QSTASH_TOKEN}`,
"Content-Type": "application/json",
},
body: JSON.stringify({
email: email,
frequency: frequencyNumber,
}),
})
.then((response) => {
if (!response.ok) {
console.error("Failed to enqueue workflow:", response.statusText);
return NextResponse.json(
{ error: "Failed to enqueue workflow." },
{ status: 500 }
);
} else {
console.log("Workflow enqueued successfully");
}
})
.catch((error) => {
console.error("Error enqueuing workflow:", error);
return NextResponse.json(
{ error: "Error enqueuing workflow." },
{ status: 500 }
);
});
return NextResponse.json({ message: "Subscription successful!" });
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error occurred:", error);
return NextResponse.json(
{ error: "An error occurred during subscription." },
{ status: 500 }
);
}
};Unsubscribe API Route
Since we have a subscription route, we need an unsubscribe route as well. When a request is made, we'll check if the user is subscribed and remove their data from Redis. We'll also send a confirmation email.
import { NextRequest, NextResponse } from "next/server";
import { redis } from "@/lib/redis";
import { sendEmail } from "@/lib/email";
export const POST = async (request: NextRequest) => {
try {
const { email } = await request.json();
if (!email) {
return NextResponse.json(
{ error: "Email is required." },
{ status: 400 }
);
}
const userExists = await redis.exists(`user:${email}`);
if (!userExists) {
return NextResponse.json(
{ error: "Email is not subscribed." },
{ status: 400 }
);
}
// Remove the user from Redis
await redis.del(`user:${email}`);
// Send an email to confirm unsubscription
await sendEmail(
"You have been unsubscribed from Upstash Newsletter.",
email
);
return NextResponse.json({ message: "You have been unsubscribed." });
} catch (error) {
console.error("Unsubscribe error:", error);
return NextResponse.json(
{ error: "An error occurred. Please try again." },
{ status: 500 }
);
}
};Workflow API Route
Now, here's the fun part! We'll create an API route that handles the workflow for sending newsletters at the specified frequency intervals.
Our workflow will do the following:
- Store the user's subscription data in Redis.
- Send a welcome email.
- Enter a loop:
- Wait for the specified frequency duration.
- Check if the user is still subscribed.
- Send the newsletter email.
- Repeat until a set number of newsletters have been sent since we don't want an infinite loop.
import { serve } from "@upstash/qstash/nextjs";
import { redis, checkSubscription, getUserFrequency } from "@/lib/redis";
import { sendEmail } from "@/lib/email";
import { SubscriptionData } from "@/types";
export const POST = serve<SubscriptionData>(async (context) => {
const { email, frequency } = context.requestPayload;
// Store the subscription in Redis
await context.run("add-user-to-redis", async () => {
console.log("Adding user to Redis");
await redis.set(`user:${email}`, JSON.stringify({ frequency: frequency }));
});
// Send a welcome email
await context.run("send-welcome-email", async () => {
console.log("Sending welcome email to", email);
await sendEmail("Welcome to Upstash Newsletter!", email);
});
// We'll send at most 3 newsletters to avoid an infinite loop
let newsletterCount = 3;
const blogPosts = [
"https://upstash.com/blog/workflow-kafka",
"https://upstash.com/blog/qstash-fifo-parallelism",
"https://upstash.com/blog/introducing-vector-database",
];
while (true) {
if (newsletterCount === 0) {
console.log("Sent desired number of newsletters. Stopping the workflow.");
break;
}
// Get user's current frequency
const currentFrequency = await context.run(
"get-user-frequency",
async () => {
console.log("Getting user's frequency");
return await getUserFrequency(email);
}
);
if (!currentFrequency) {
console.log("User is not subscribed anymore. Stopping the workflow.");
break;
}
// Wait for the frequency to send the next email
await context.sleep(
"wait-for-user-frequency",
60 * 60 * 24 * currentFrequency // Convert days to seconds
);
// Check if the user is still subscribed
const exists = await context.run("check-user-subscription", async () => {
console.log("Checking if user is still subscribed");
return await checkSubscription(email);
});
if (!exists) {
console.log("User is not subscribed anymore. Stopping the workflow.");
break;
}
// Send the newsletter email
await context.run("send-newsletter-email", async () => {
console.log("Sending newsletter email to", email);
await sendEmail(
`
Read this newsletter's blog post: ${blogPosts[newsletterCount - 1]}
You are receiving this email because you subscribed to Upstash Newsletter.
You can unsubscribe anytime by clicking the link below.
You have ${newsletterCount} newsletters left.
Unsubscribe here: ${process.env.NEXT_PUBLIC_BASE_URL}/unsubscribe?email=${email}
`,
email
);
});
newsletterCount--;
}
return;
});Here's an example of a completed workflow for a user who subscribed, received a single newsletter, and unsubscribed:
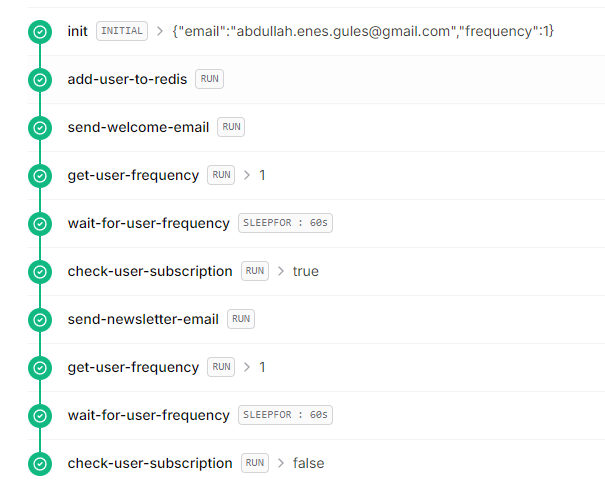
You can access and monitor your workflows from the Upstash Console.
Main Page Component
Let's set up the main page of our application. This page will include the subscription form and a link to the unsubscribe page.
import SubscriptionForm from "@/components/SubscriptionForm";
import Link from "next/link";
export default function Home() {
return (
<main className="flex flex-col items-center justify-center min-h-screen p-4">
<h1 className="text-3xl font-bold mb-6">
Subscribe to Upstash Newsletter
</h1>
{/* Subscription Form */}
<SubscriptionForm />
{/* Unsubscribe Link */}
<div className="mt-8">
<p className="text-gray-600">
Already subscribed and want to unsubscribe?
<Link
href="/unsubscribe"
className="text-red-500 hover:text-red-700 font-bold ml-2"
>
Click here to unsubscribe
</Link>
</p>
</div>
</main>
);
}Unsubscribe Page Component
Finally, let's create the unsubscription page.
import UnsubscribePage from "@/components/UnsubscribeForm";
export default function UnsubscribeHome() {
return (
<main className="flex flex-col items-center justify-center min-h-screen p-4">
<h1 className="text-3xl font-bold mb-6">
Unsubscribe from Upstash Newsletter
</h1>
{/* Unsubscribe Form */}
<UnsubscribePage />
</main>
);
}Conclusion
And there you have it! We've built a simple newsletter app without worrying about serverless function timeouts.
You can find the complete source code for this project on GitHub and you can check out the live demo here.
For more information on Upstash Workflow, you can refer to the Upstash Documentation.
If you have any questions, feel free to reach out to us on Discord. Also, don't forget to explore the Upstash Blog for more tutorials and use cases.
