Optimize LLM Applications: Semantic Caching for Speed and Savings
Imagine you have an LLM-powered chatbot managing customer support inquiries. Whether you’re using OpenAI or a similar provider, as traffic grows, so do your costs, since most providers charge based on token usage. In this post, we’ll explore how semantic caching can help you cut these costs while also boosting the speed and responsiveness of your applications.
Let’s walk through a typical scenario: A user asks, 'How do I reset my password?' You send the query to your Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) pipeline, retrieve the answer from your LLM, and display it to the user. Everything works smoothly.
Later, a second user asks, 'What should I do if I forgot my password?' You again send the query to the same pipeline, receive almost the exact same answer from the LLM, and present it to the user.
Here’s the issue: You’ve now used your LLM twice to generate essentially the same response. While a traditional cache could help detect duplicate queries, it would struggle in this case because the two questions are lexically different. They are only similar in meaning, not in structure. To solve this, you need a caching system that recognizes semantic similarity rather than relying on exact string matches. This is where semantic caching comes into play—reducing redundant LLM calls and cutting costs while keeping response times fast.
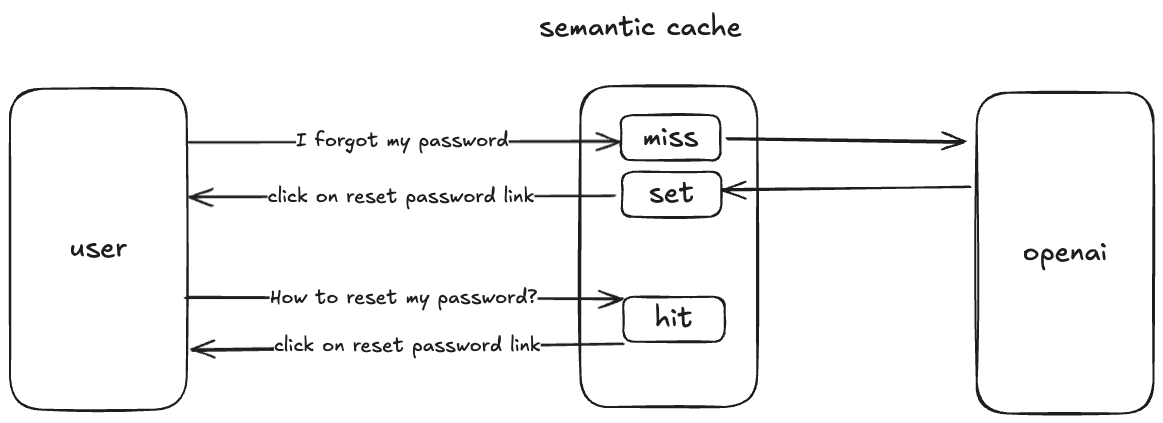
Semantic cache is a caching system that stores key-value pairs and returns the same value for keys with similar meanings. Instead of relying on exact string matches, it uses a vector database to determine the semantic similarity between keys. If the similarity score meets a predefined threshold, the cache returns the stored value (hit); otherwise, it treats it as a miss.
Upstash offers an open-source implementation of Semantic Cache, powered by Upstash Vector. This solution simplifies the process by generating embeddings directly within Upstash Vector, eliminating the need for external embedding tools.
One of its key features is the minProximity parameter, which allows you to control the similarity threshold. A higher minProximity value requires a closer match between user input and cached content to count as a hit. For example, a proximity score of 0.95 reflects high similarity, while a score of 0.75 captures lower similarity. If set to 1.00—the maximum value—only an exact match between the user query and cached entry will be treated as a hit.
Check out the repo for more about the Upstash Semantic Cache.
JS/TS repo: https://github.com/upstash/semantic-cache
Python repo: https://github.com/upstash/semantic-cache-py
Example:
import { SemanticCache } from "@upstash/semantic-cache";
import { Index } from "@upstash/vector";
// 👇 your vector database
const index = new Index();
// 👇 your semantic cache
const semanticCache = new SemanticCache({ index, minProximity: 0.95});
await semanticCache.set("largest city in USA by population", "New York");
await delay(1000);
// 👇 outputs "New York"
const result = await semanticCache.get("which is the most populated city in the USA?");Code Breakdown
Creating the Vector Index
const index = new Index()- This initializes the vector index. It will store the embeddings for each key (query) used in the cache.
Creating the Semantic Cache
const semanticCache = new SemanticCache({ index, minProximity: 0.95 });- This creates an instance of the semantic cache connected to the vector index.
minProximity: 0.95: This parameter sets the similarity threshold. Only queries with a similarity score of 0.95 or higher will result in a cache hit.
Setting a Cache Entry
await semanticCache.set("largest city in USA by population", "New York")- Stores the key-value pair:
- Key:
"largest city in USA by population" - Value:
"New York"
- Key:
- An embedding is generated for the key and saved in the vector index.
Introducing a Delay
await delay(1000);- This simulates a 1-second pause, similar to real-world scenarios where different users ask queries at different times.
Retrieving a Value with a Similar Query
const result = await semanticCache.get("which is the most populated city in the USA?");
// 👇 outputs "New York"
console.log(result);- Although the new quey is not an exact string match, it is semantically similar to the cached key.
- The vector index calculates the similarity between the stored key and the new query. If the score exceeds the
minProximitythreshold (0.95), the cached value is returned.
Conclusion
Semantic caching enhances LLM-powered applications by recognizing meaning-based similarities, reducing redundant API calls, and cutting costs. Unlike traditional caches, it uses vector databases to match semantically similar queries, improving both speed and efficiency.
Upstash Semantic Cache is an open source implementation of semantic cache and it can be used with a Upstash Vector Database. Get started today by exploring the open-source repos:
Follow us on twitter for more posts like this.
