Kafka is a messaging and stream processing platform with many use cases. In this post we will talk about the use cases most relevant to web applications.
Website Activity Tracking
You can track your user’s behaviour on your website using Kafka. You send all types of activities (clicks, searches, scrolls, form submissions) to different Kafka topics. Once you have all activity data in your Kafka, you can consume data to process it for real-time monitoring, real-time processing, and loading to a data warehouse for advanced analytics.
Example: Dynamic Promotion for Ecommerce Sites
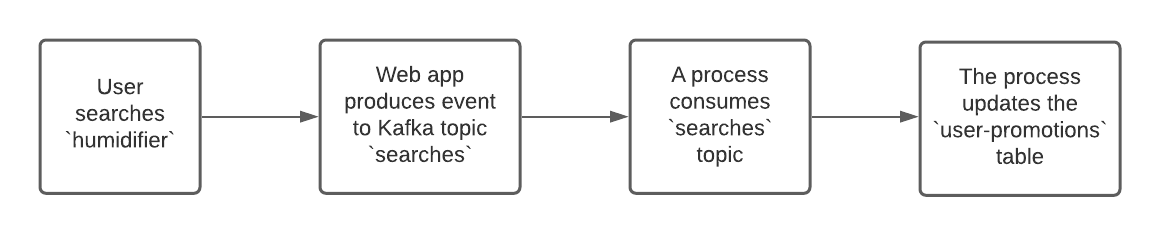
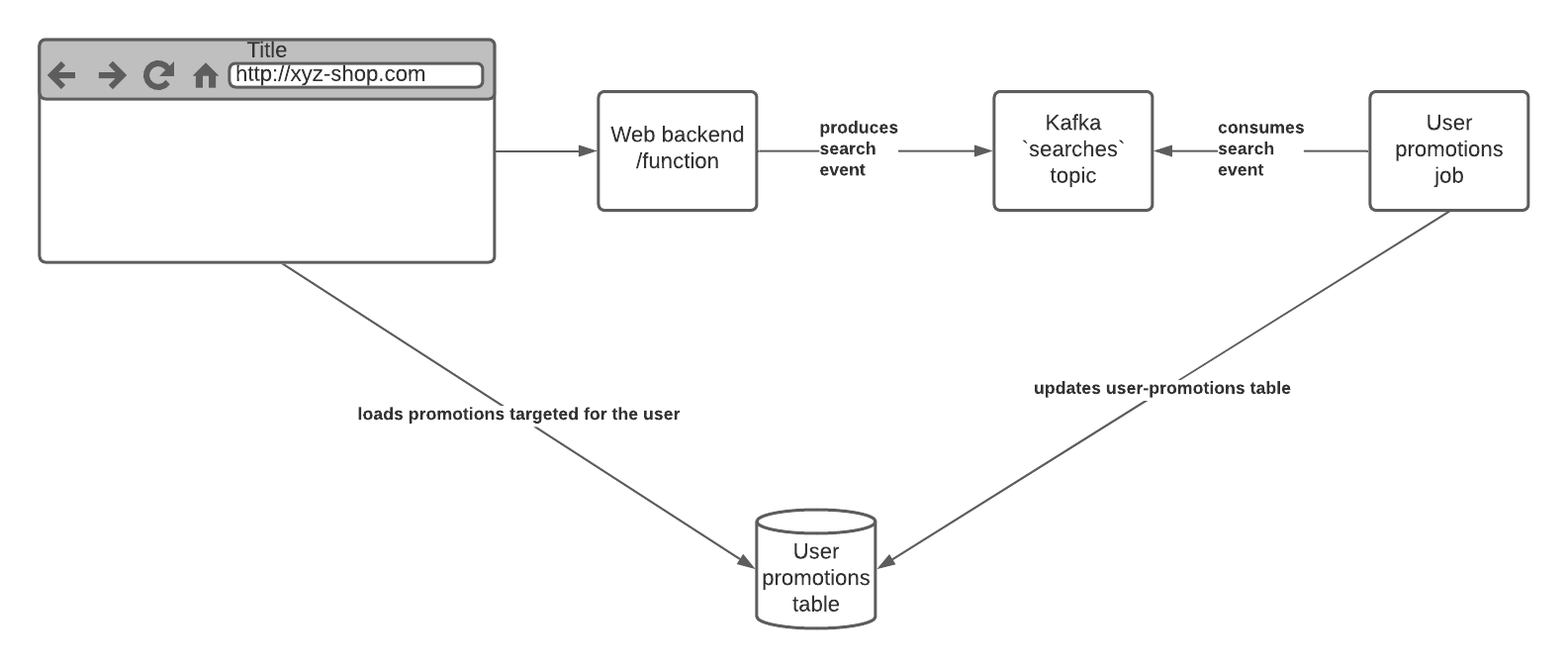
Scenario: You have an ecommerce site. In your website, a user searches with the keyword humidifier. You want to show humidifier deals on your home page for this user.
When a user enters the keyword, the backend which processes the request will produce a message to a Kafka topic. Another process will be consuming the topic and it will update the user_promotions table according to the information consumed. The user_promotions table keeps the information about what promotion should be displayed to each user.
Sample Message:
{
“user_id” : “[abcde@gmail.com](mailto:abcde@gmail.com)”,
“page_url” : “/deals/”
“search_keyword” : “humidifier”,
“date” : 1640912388090
}
Log Aggregation
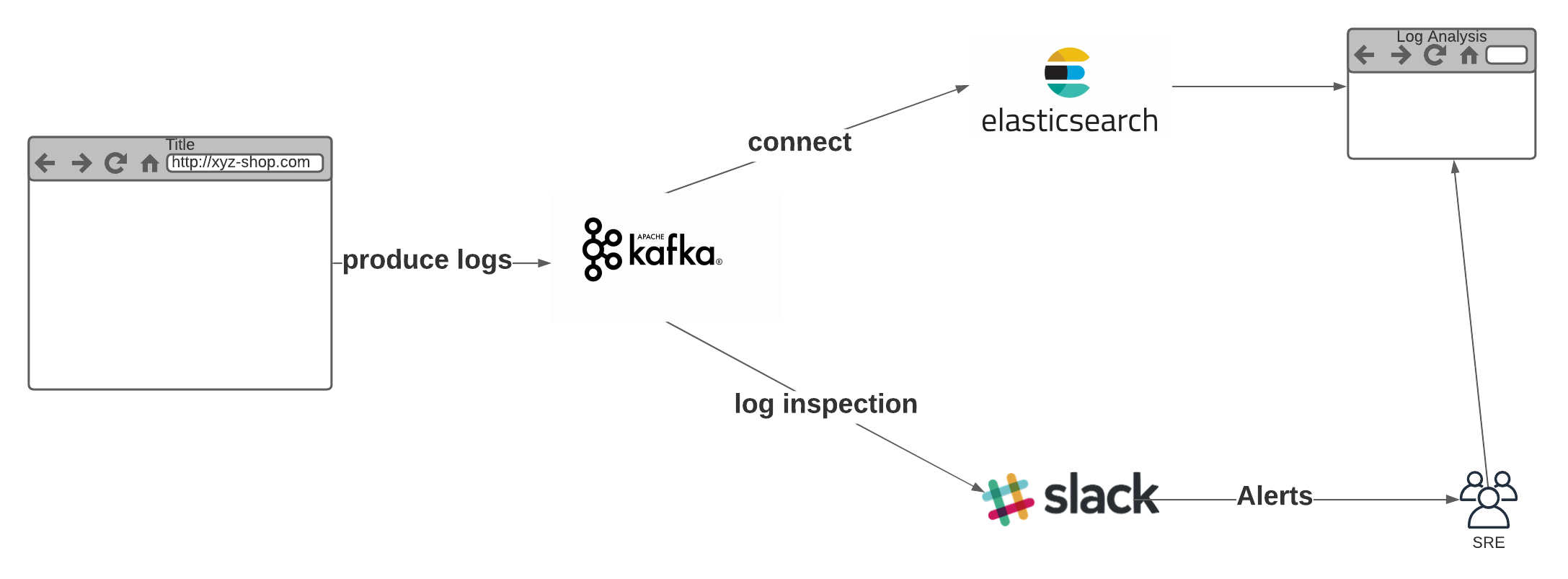
You can use Kafka as the central place to keep your web application’s logs. Then you can process your backend’s logs to create alerts and you can move the logs to a log analysis tool for reporting purposes. Because you keep the logs at Kafka, you can change your Log analysis tool when you want. You can also run processes which analyzes the logs and trigger alerts to the relevant teams.
Content Moderation
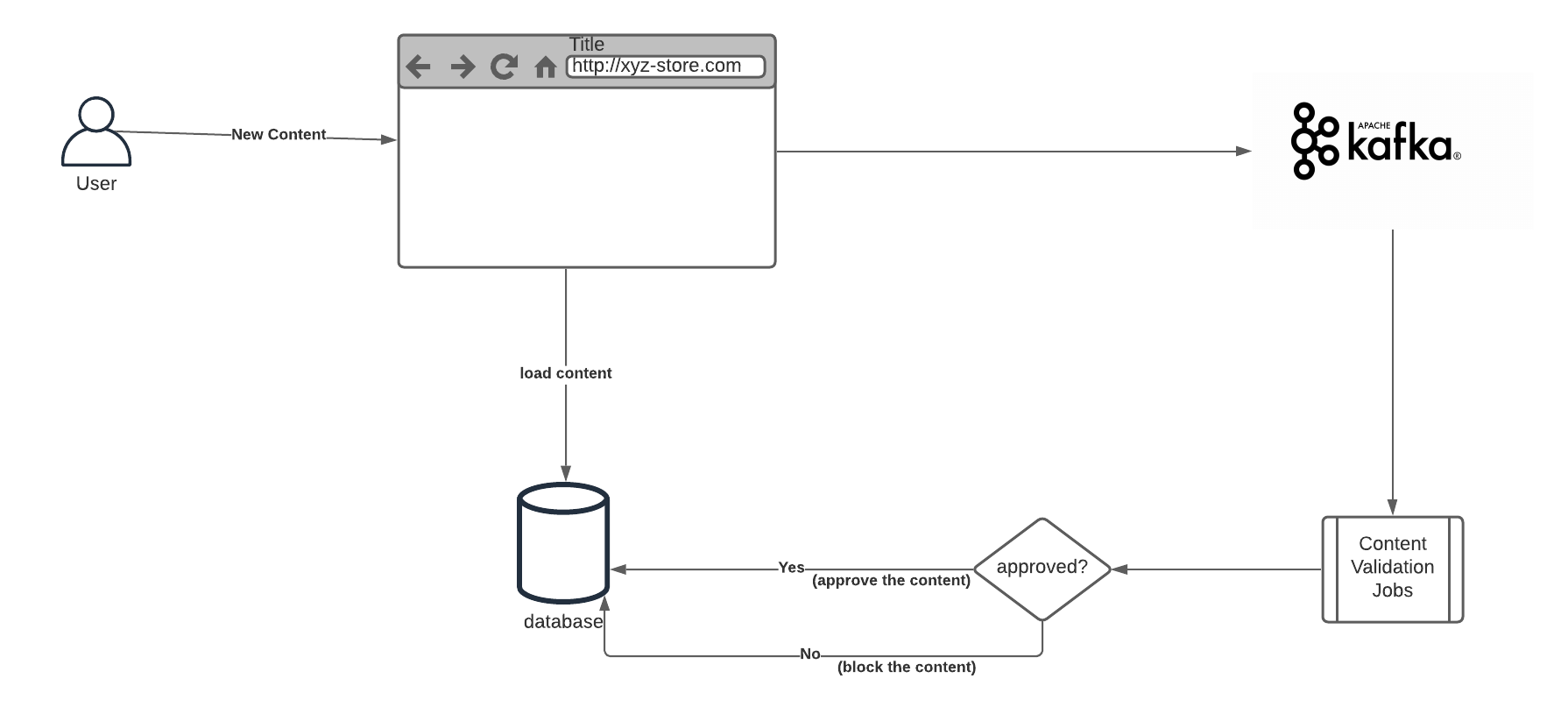
You have a website with user generated content. For example an ecommerce site where users add product reviews. You will want to hide or block the fake reviews and the ones against your content rules. Here some requirements:
- Content moderation should be asynchronous to content creation. Namely, the user should not wait for the validation while adding new content.
- Content moderation should not be coupled with web application. You should be able to update or change the moderation without touching the web application flow.
- You may want to re-validate all the past content when you update your content moderation system.
An architecture with Kafka helps you to satisfy the above requirements. Keeping the new content in the Kafka helps you to decouple your content moderation from your web application.
When a user adds a new content its state will be as pending, so it will be only visible to its author. After the validation jobs approves the content, its change will be changed to approved so it will be publicly available.
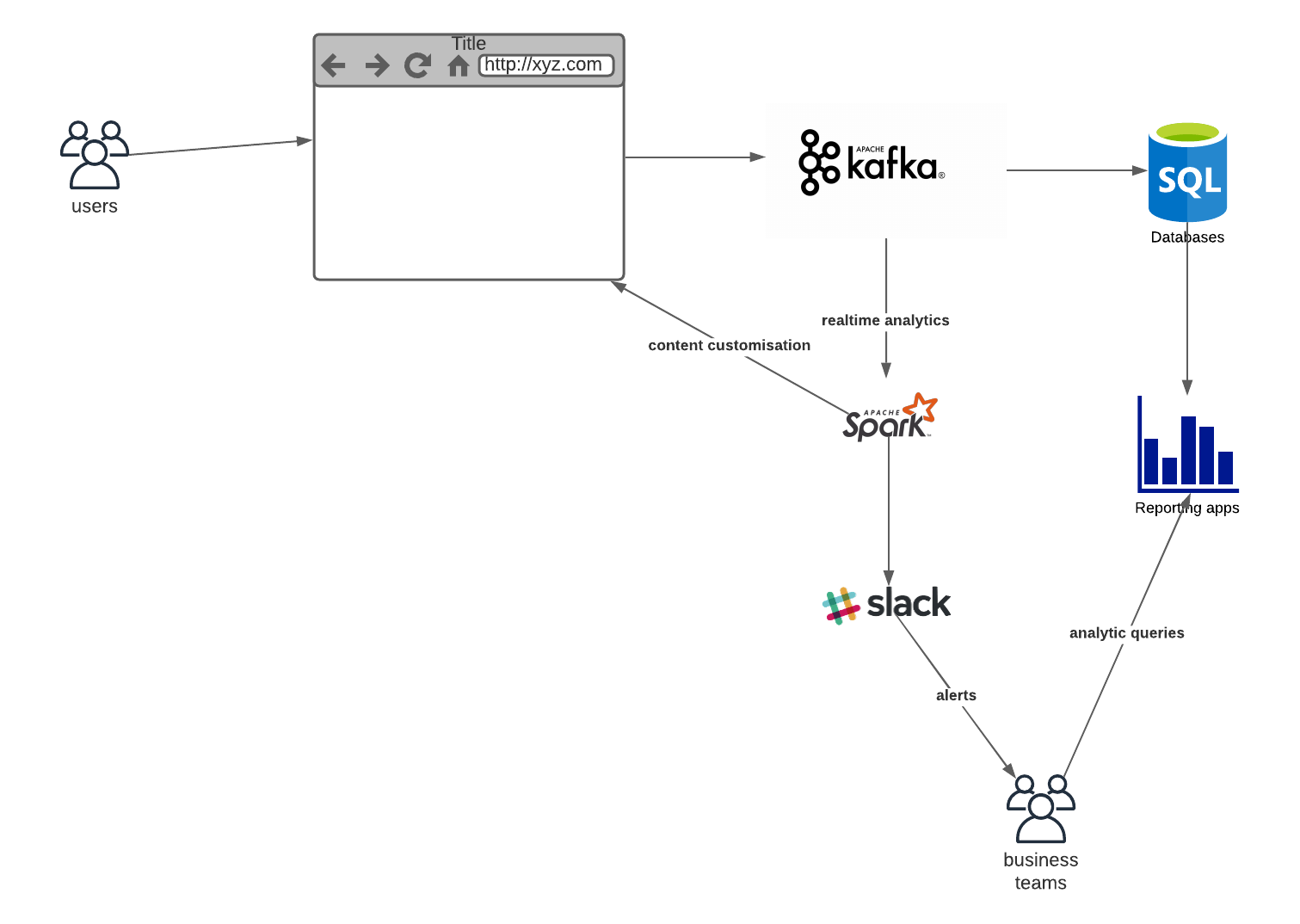
Website Analytics
This use case is a superset of activity tracking. This time we collect the users’ behaviour and save them in a database which allows analytical processing. We can create further tools for the business teams for reporting purposes. Thanks to Kafka we can also run real time processes on the same data.
Conclusion
In this post, we briefly described the most popular use cases of Kafka for web developers. In the following posts, we will implement examples for these use cases using Upstash Kafka. Waiting for your feedback on Twitter and Discord.
