How to Create an AI Postcard Sender with Upstash QStash
In this article, we will look at how to make an AI Postcard sending app at a high level. We will focus mainly on scheduling tasks with Upstash QStash, a serverless message queue and task scheduler.
This app uses the Next.js 13 App Router (hosted on Vercel), Upstash QStash for task scheduling, Upstash Redis for cache, Replicate AI for SDXL image generation, and Resend for HTTP email sending.
Project Setup
Go ahead and create a new Next.js project using the CLI. Make sure to enable the App Router. Configure the rest of the app as you like. This article will be using tailwindCSS and typescript. Feel free to reference the source code for this project on GitHub.
npx create-next-app@latest
Install all necessary dependencies for this project:
npm install @upstash/qstash @upstash/redis replicate resend
Now that you have everything installed, go ahead and deploy the project to Vercel!
Environment Variable Configuration
Create an .env file in the root of your Next.js project. Go ahead and add the following variables:
REPLICATE_API_TOKEN=
UPSTASH_REDIS_REST_URL=
UPSTASH_REDIS_REST_TOKEN=
QSTASH_URL=
QSTASH_TOKEN=
RESEND_API_KEY=Make sure that you add your environment variables within Vercel in your project settings as well! Otherwise the app will not work.
NOTE: To get all of these values, you will need an account with each of the services. But don't worry, they are free!
Pay attention to the domain that your app is deployed on. This could be your own custom domain if you configured it, or a default one given by Vercel. We will need this domain for later in the project.
App Architecture
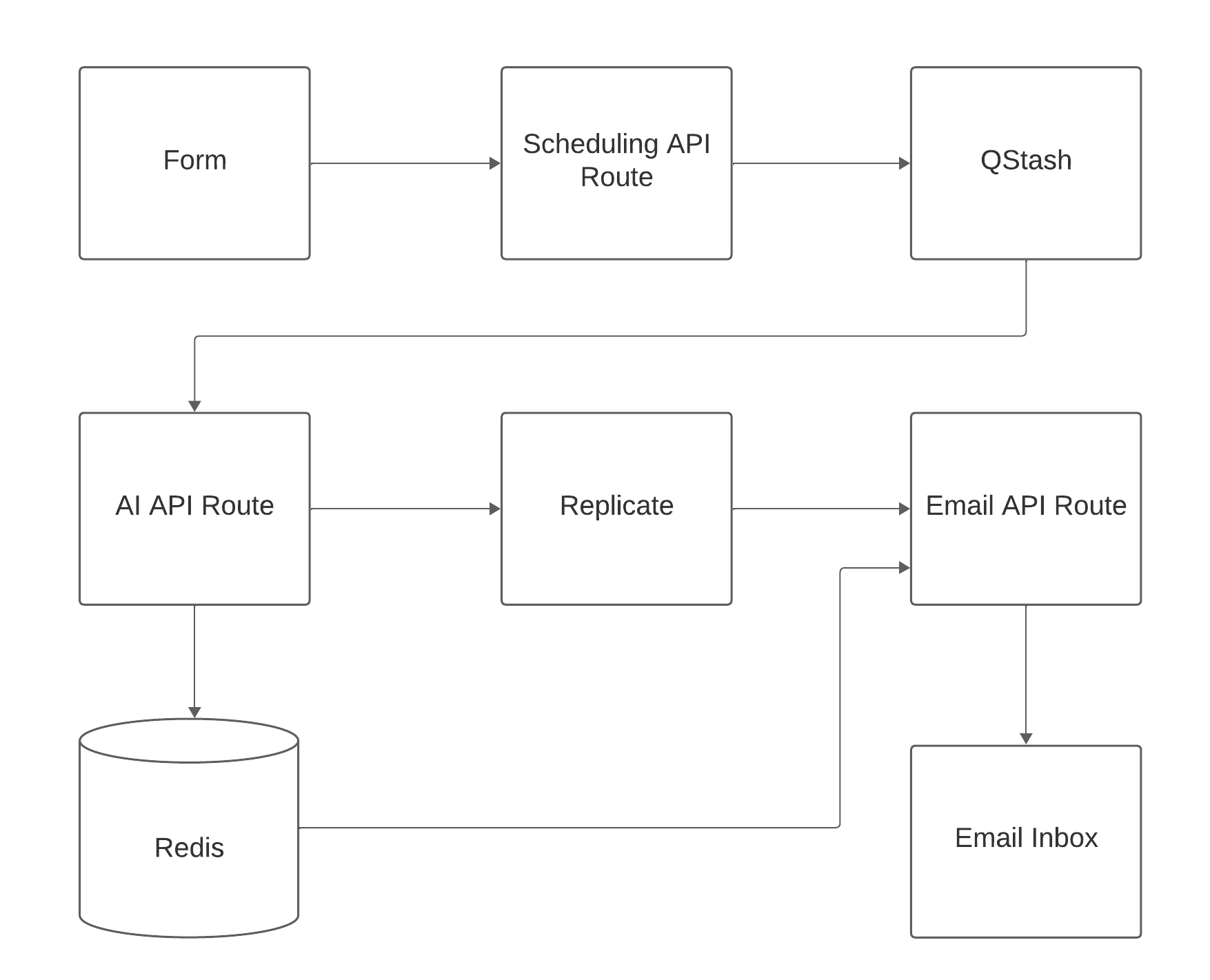
How that we have our project deployed to Vercel and are ready to start building, let's quickly go over the app architecture. Here is the flow of the app:
- A user fills out a form with an email address for the recipient, a body message for the email, a prompt for the image, and sets a date and a time of day to send the postcard.
- We handle the form submission on an API route and publish a message to QStash.
- When the specified time approaches, QStash sends the message to another API route in our app. This API route catches the message from QStash, sends a request to Replicate to generate the image, and caches the ID of the Replicate generation in Redis with our email information.
- Once the image is finished generating, Replicate sends a webhook to another API route in our app. This route catches the webhook and retrieves the cached information from Redis by the Replicate generation ID. This key value pair includes all necessary info for the email. We then send an email using Resend to the postcard recipient with the image attached.
Making the Form
Now that we have an idea of how the app works, let's dive into writing some code!
We'll start by creating the form. To create a nice looking form quickly, I am using shadcn/ui. However, you can use whatever you would like to create the form!
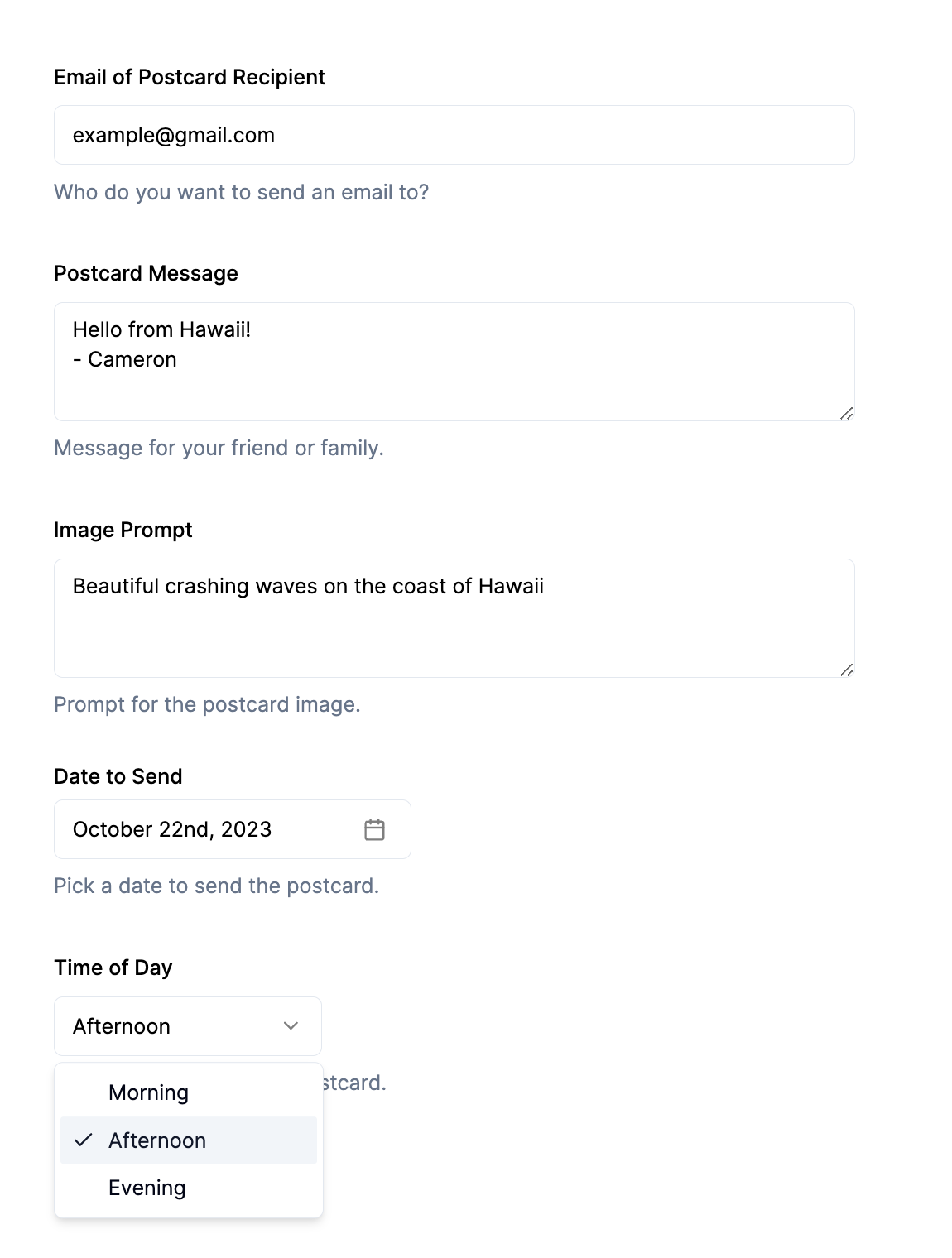
In a components directory in the root of your project, go ahead and create the file form.tsx. This form will have 5 inputs:
- Email address of the recipient
- Message for the postcard (email body)
- Prompt for the image
- Date to send the postcard (limited to the next 7 days)
- Time of day to send (limited to morning, afternoon, and evening)
Here is a shortened version of the form I created. Reference the GitHub repository for the full code:
export default function MainForm() {
const onSubmit = async (values: z.infer<typeof formSchema>) => {
const timeMapping: Record<TimeKey, number> = {
morning: 9,
afternoon: 12,
evening: 18,
};
const hour = timeMapping[values.time as TimeKey];
const date = new Date(values.date);
date.setHours(hour, 0, 0, 0);
const timestamp = date.getTime() / 1000;
const combinedValues = { ...values, timestamp };
console.log(combinedValues);
const response = await fetch("/api/schedule", {
method: "POST",
body: JSON.stringify(combinedValues),
});
};
return (
<>
<Form {...form}>
<form
onSubmit={form.handleSubmit(onSubmit)}
className="space-y-8 w-full"
>
<FormField
control={form.control}
name="email"
render={({ field }) => (
<FormItem>
<FormLabel>Email of Postcard Recipient</FormLabel>
<FormControl>
<Input placeholder="example@gmail.com" {...field} />
</FormControl>
<FormDescription>
Who do you want to send an email to?
</FormDescription>
<FormMessage />
</FormItem>
)}
/>
<FormField
control={form.control}
name="message"
render={({ field }) => (
<FormItem>
<FormLabel>Postcard Message</FormLabel>
<FormControl>
<Textarea placeholder="Dear Friend..." {...field} />
</FormControl>
<FormDescription>
Message for your friend or family.
</FormDescription>
<FormMessage />
</FormItem>
)}
/>
<FormField
control={form.control}
name="prompt"
render={({ field }) => (
<FormItem>
<FormLabel>Image Prompt</FormLabel>
<FormControl>
<Textarea
placeholder="A beautiful ocean view..."
{...field}
/>
</FormControl>
<FormDescription>
Prompt for the postcard image.
</FormDescription>
<FormMessage />
</FormItem>
)}
/>
<FormField
control={form.control}
name="date"
render={({ field }) => (
<FormItem className="flex flex-col">
<FormLabel>Date to Send</FormLabel>
<Popover>
<PopoverTrigger asChild>
<FormControl>
<Button
variant={"outline"}
className={cn(
"w-[240px] pl-3 text-left font-normal",
!field.value && "text-muted-foreground"
)}
>
{field.value ? (
format(field.value, "PPP")
) : (
<span>Pick a date</span>
)}
<CalendarIcon className="ml-auto h-4 w-4 opacity-50" />
</Button>
</FormControl>
</PopoverTrigger>
<PopoverContent className="w-auto p-0" align="start">
<Calendar
mode="single"
selected={field.value}
onSelect={field.onChange}
disabled={(date) => {
const today = new Date();
today.setHours(0, 0, 0, 0);
const nextWeek = new Date();
nextWeek.setDate(today.getDate() + 7);
return date > nextWeek || date < today;
}}
initialFocus
/>
</PopoverContent>
</Popover>
<FormDescription>
Pick a date to send the postcard.
</FormDescription>
<FormMessage />
</FormItem>
)}
/>
<FormField
control={form.control}
name="time"
render={({ field }) => (
<FormItem>
<FormLabel>Time of Day</FormLabel>
<FormControl>
<Select
onValueChange={field.onChange}
defaultValue={field.value}
>
<SelectTrigger className="w-[180px]">
<SelectValue placeholder="Time of day" />
</SelectTrigger>
<SelectContent>
<SelectItem value="morning">Morning</SelectItem>
<SelectItem value="afternoon">Afternoon</SelectItem>
<SelectItem value="evening">Evening</SelectItem>
</SelectContent>
</Select>
</FormControl>
<FormDescription>
Time of day to send the postcard.
</FormDescription>
<FormMessage />
</FormItem>
)}
/>
<Button variant="outline" type="submit">
Submit
</Button>
</form>
</Form>
</>
);
}
Then, add the form to your main page.tsx file in the app directory:
import MainForm from "@/components/form";
export default function Home() {
return (
<main className="flex min-h-screen flex-col items-center justify-between p-24">
<MainForm />
</main>
);
}There's one key piece of this code we should point out. In the onSubmit function, We are creating a timestamp variable that has a UNIX datetime that will specify when we want the postcard to send. We are combining the date from a datepicker component with a time of day that the user selects. Make sure that this timestamp is in seconds, not milliseconds.
Making the API Routes
We will make 3 API routes for this project:
/api/schedule/api/ai/api/email
Let's start with the first one. Create the file route.ts in your app/api/schedule directory. Add the following code:
type RequestBody = {
email: string;
prompt: string;
message: string;
timestamp: number;
};
import { Client } from "@upstash/qstash";
import { NextResponse } from "next/server";
const qstashClient = new Client({
token: process.env.QSTASH_TOKEN || "",
});
export async function POST(request: Request) {
const body: RequestBody = await request.json();
const host = request.headers.get("host");
const qstashResponse = await qstashClient.publishJSON({
url: `https://${host}/api/ai`,
body: body,
notBefore: body?.timestamp,
});
return NextResponse.json(qstashResponse);
}In this route, we are grabbing the data pushed through the form and publishing it as a message to QStash. In our message, we pass the URL that QStash will send our message to. Since this is our own API route, we will use the host header to grab our domain and pass it in the url. We also add a parameter notBefore. This is where we pass in the timestamp we created to tell QStash when to send the message.
Let's create the next API route. Create a route.ts file in app/api/ai and add the following code:
import { NextResponse } from "next/server";
import Replicate from "replicate";
const redis =
!!process.env.UPSTASH_REDIS_REST_URL && !!process.env.UPSTASH_REDIS_REST_TOKEN
? new Redis({
url: process.env.UPSTASH_REDIS_REST_URL,
token: process.env.UPSTASH_REDIS_REST_TOKEN,
})
: undefined;
const replicate = new Replicate({
auth: process.env.REPLICATE_API_TOKEN || "",
});
export async function POST(request: Request) {
try {
const body: RequestBody = await request.json();
const output = await replicate.predictions.create({
version:
"563a66acc0b39e5308e8372bed42504731b7fec3bc21f2fcbea413398690f3ec", // CHANGE THE MODEL IF DESIRED
input: {
prompt: "In the style of HISGH. " + body.prompt
},
webhook: "https://example.com/api/email", // CHANGE THIS TO YOUR GIVEN DOMAIN IN VERCEL
});
await redis!.hset(output?.id, body);
return NextResponse.json(output);
} catch (error) {
console.log(error);
return NextResponse.json("An error occurred. Please try again later.", {
status: 500,
});
}
}
Let's break this code down. We create instances of Redis and Replicate and grab the post data from the QStash message. Then, we create a prediction using Replicate and set a webhook URL. Note: Make sure to set this URL as your assigned domain in Vercel plus the correct API route. Finally, we cache the body of the QStash message in Redis with the ID of the Replicate prediction.
For the final API route, create a route.ts file in app/api/email and add the following code:
type Postcard = {
email: string;
message: string;
};
import { NextResponse } from "next/server";
import { Prediction } from "replicate";
import redis from "@/lib/redis";
import resend from "@/lib/resend";
import { EmailTemplate } from "@/components/email";
export async function POST(request: Request) {
const body: Prediction = await request.json();
const postcard = (await redis?.hgetall(body?.id)) as Postcard;
const data = await resend.emails.send({
from: "onboarding@resend.dev",
to: [postcard?.email],
subject: "AI POSTCARD!!!",
react: EmailTemplate({
message: postcard?.message,
image: body?.output[0],
}) as React.ReactElement,
});
return NextResponse.json(data);
}This simple API route catches the webhook that Replicate sends. Using the ID of the Replicate prediction sent in the webhook body, we retrieve the cached data that includes the email recipient and body. Lastly, we send an email using Resend with the AI image in the body.
But wait... You may be wondering what the EmailTemplate is. Well, Resend actually allows us to define emails as JSX. So, before you test your app, make sure to add an email.tsx file in your components directory that looks something like this:
import * as React from "react";
interface EmailTemplateProps {
message: string;
image: string;
}
export const EmailTemplate: React.FC<Readonly<EmailTemplateProps>> = ({
message,
image,
}) => (
<div>
<img src={image} width={100} height={100} alt="Postcard image." />
<p>{message}</p>
</div>
);This is a very simple example, so feel free to customize your email component.
And that's it! We should be good to now test our app. After you push your code to Vercel, go ahead and submit a test postcard. In QStash, you will now see a new message that is waiting to be sent to the endpoint we specified.
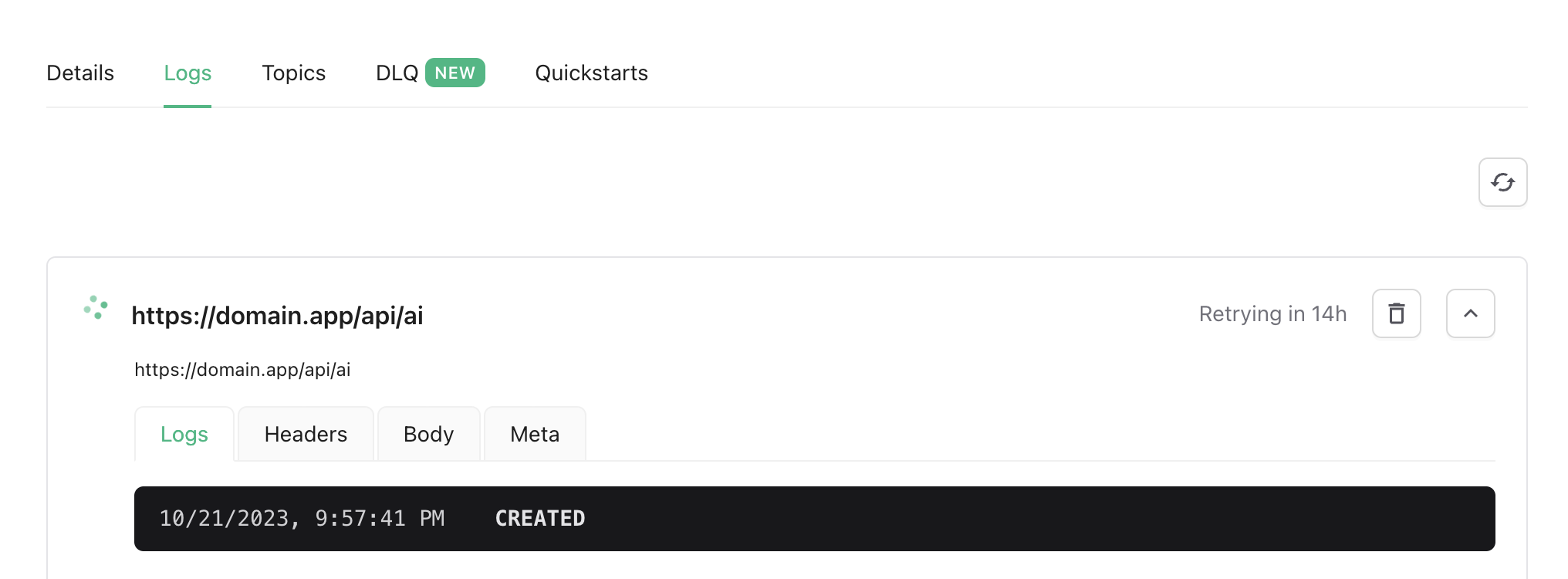
Once it sends, it will trigger the AI image generation in Replicate. You can also see the generation status within the Replicate dashboard. Finally, Replicate will send a webhook to our email endpoint which will send an email with the generated image! Pretty cool, right?
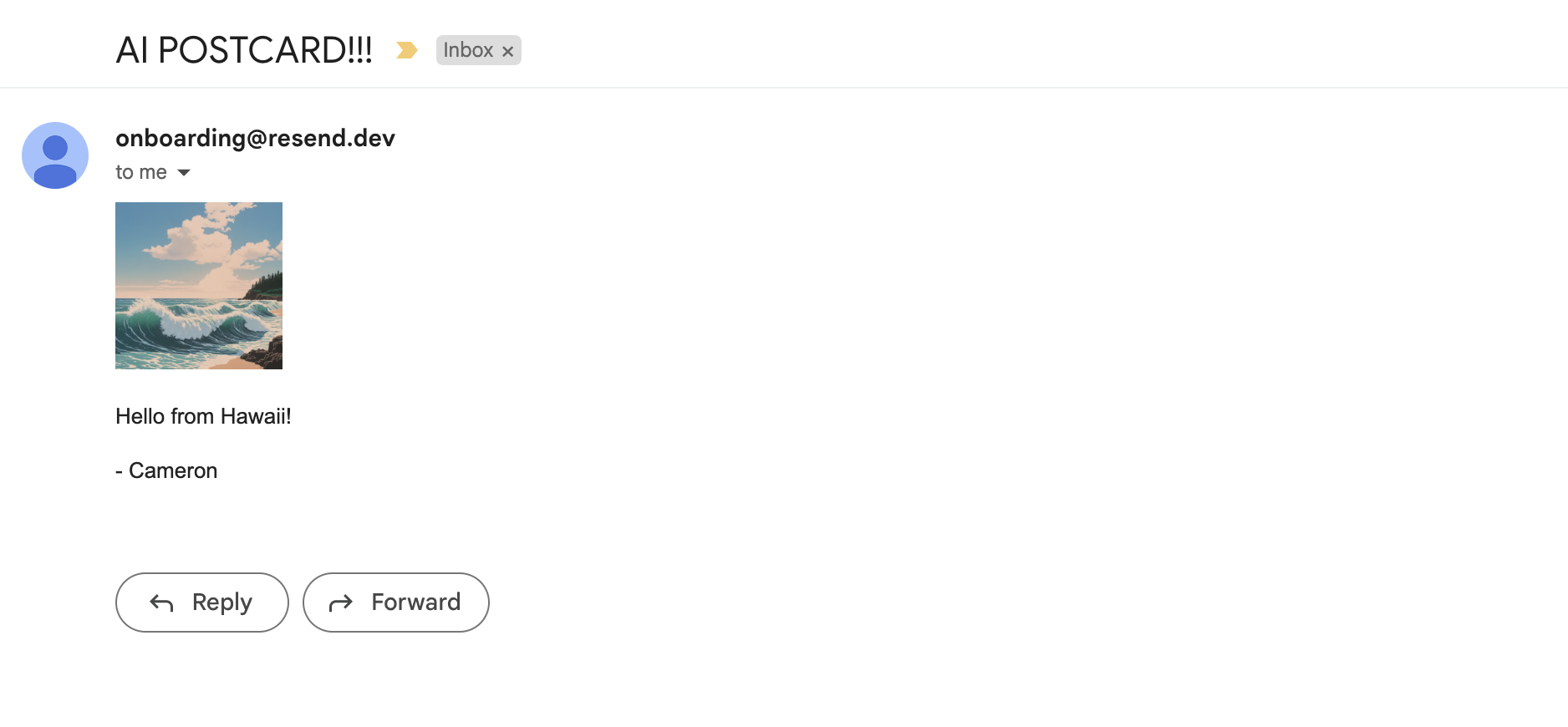
Note for emails: If you don't see the email right away but are expecting it, make sure to check your spam.
QStash and Upstash Redis
QStash and Redis enabled us to make this app with ease! Queues, schedules, and cache can be complex pieces to implement in an app, but thanks to Upstash, we were able to easily incorporate them in the best full-stack React framework! Not to mention, it only took a couple of lines of code using their well thought out SDKs.
Possible Improvements
While we skipped over it in this article, it's a best practice to verify the request coming from QStash to validate that it is safe. Here are the docs on how to do that.
Verify your domain in Resend. By default, you will only be able to send emails to yourself in Resend. To send emails to other recipients, you will need to add a domain and verify it.
While we are using one specific SDXL model on Replicate, there are many other models to choose from. Change the model ID in the api/ai route and update the parameters to change the model.
About the Author
Cameron Youngblood is a Full Stack Developer at Ampry Software and a contributor to Alpine Codex.
Star this project on GitHub!
